Improving Population Health with Remote Patient Monitoring for Diabetes
According to the 2022 National Diabetes Statistics Report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) there are an estimated 130 million adults living with diabetes or prediabetes in the United States, that’s about one in three individuals (1). This alarming rate has a direct impact on healthcare resources and demonstrates the need for better care models targeting those at risk for disease development and complication (2).
The High Cost of Diabetes
Diabetes is the most expensive chronic condition across the nation (2)
$1 out of every $4 in US health care dollars are spent caring for people with diabetes (2)
$237 billion is spent each year on direct medical costs and another $90 billion on reduced productivity (2)
The total economic cost of diabetes rose 60% from 2007 to 2017 (2)
61% of diabetes costs are for people 65 years or older, which is mainly paid by Medicare (2)
48% to 64% of lifetime medical costs for a person with diabetes are for complications related to diabetes, such as heart disease and stroke (2)
Strategies That Work: Remote Patient Monitoring & Virtual Care
Given the heavy impact on healthcare, solutions are needed that can deliver affordable, evidence-based programs that promote lifestyle changes in population cohorts most at risk for disease progression and complication.
Mozzaz provides patient-centric solutions through our Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) platform with programs specifically designed to monitor, educate and guide patients through their illness and act as a digital landscape for their care-plan.
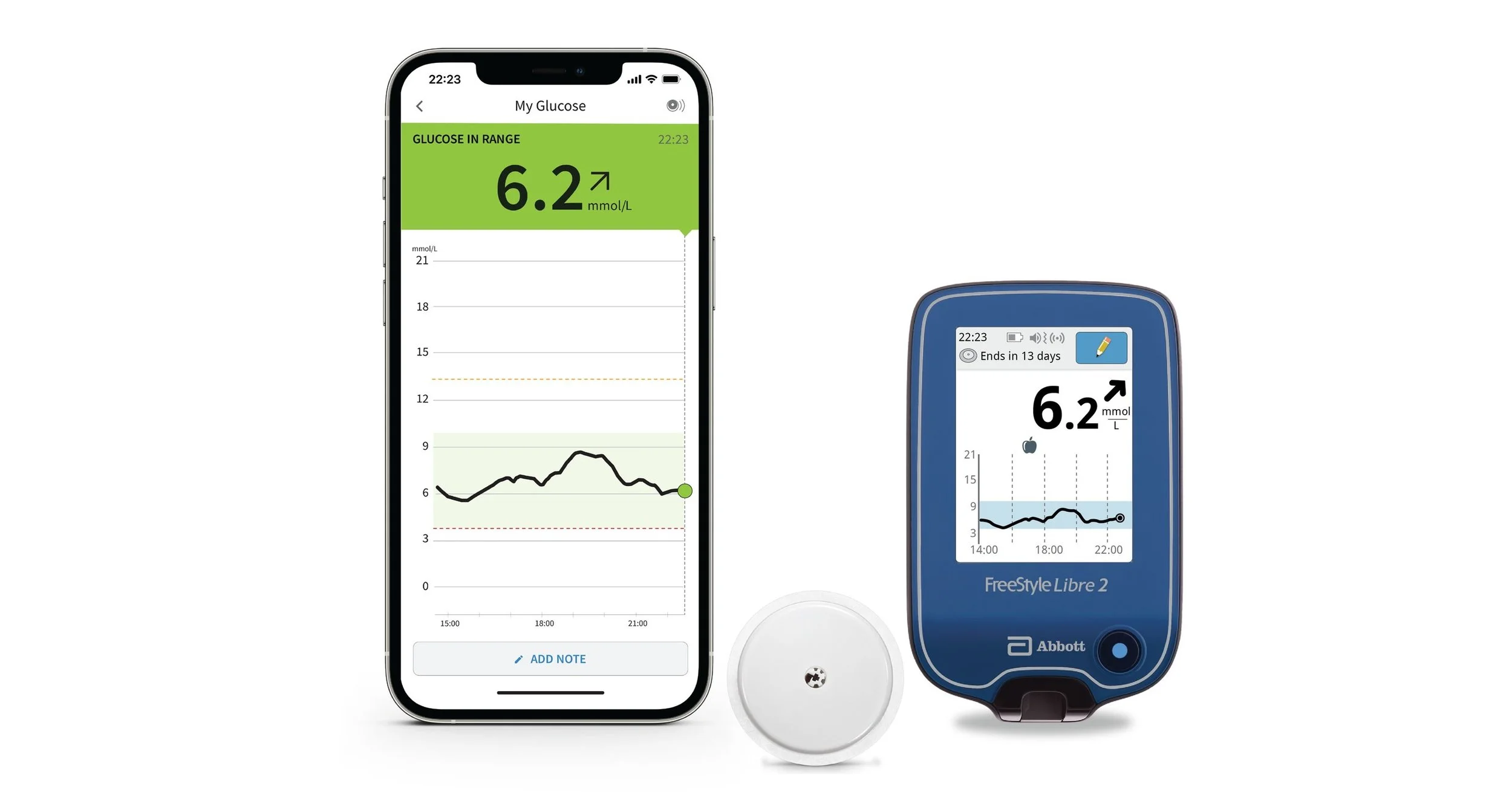
Featuring compatibility with the latest-and-greatest Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) devices, such as Dexcom and Abbott’s FreeStyle Libre products, patients can directly benefit from higher quality care. The Mozzaz Platform can be directly integrated into the provider’s Electronic Health Records (EHR) for full interoperability. Depending on the patient’s needs, additional devices such as blood pressure monitors or weight scales may also be added – providing actionable insights at your fingertips for both the patient and provider.
Successful program implementations may be expected to produce the following results:
Lifestyle change programs can reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by more than 50% for people at high risk (2)
Effective blood sugar management can reduce the risk of eye disease, kidney disease, and nerve disease by 40% (2)
Blood pressure management can reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke by 33% to 50%. Improved cholesterol levels can reduce cardiovascular complications by 20% to 50% (2)
Regular eye exams and timely treatment could prevent up to 90% of diabetes-related blindness (2)
Health care services that include regular foot exams and patient education could prevent up to 85% of diabetes-related amputations (2)
Detecting and treating early diabetic kidney disease by using kidney protective medicines that lower blood pressure can reduce decline in kidney function by 33% to 37% (2)
About Mozzaz
Mozzaz has a proven track record of producing industry leading virtual care and remote patient monitoring solutions that improve the access to care for your patients, drive better population health outcomes and help you better manage costs associated with your most at-risk population groups.
Our platform includes the innovative Adaptive Intervention Modeler (AIM™) which allows healthcare organizations to drive data-driven actions with rule-based content and smart alerts. This unique digital health technology enables patient-centric solutions for even the most complex care populations, driving continuous engagement and better patient outcomes.
If you are interested in exploring what a virtual care or remote patient monitoring solution would look like for your organization, contact us today.
References:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report website. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html. Accessed October 17, 2022.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Cost-Effectiveness of Chronic Disease Interventions website. https://www.cdc.gov/chronicdisease/programs-impact/pop/diabetes.htm. Accessed October 17, 2022.